- 1. Summary – A Guide to a Balance and Healthy Diet
- 2. A. Understanding the Importance of a Balanced Diet
- 3. B. Key Components of a Balanced Diet
- 4. C. Achieving Balance and Variety
- 5. D. Evidence-Based Benefits of a Balanced Diet
- 6. II. Benefits of a Balanced and Healthy Diet
- 7. A. Protein:
- 8. B. Carbohydrates:
- 9. C. Healthy Fats:
- 10. D. Vitamins and Minerals:
- 11. E. Water:
- 12. IV. Eating Habits for a Balanced and Healthy Diet
- 13. A. Meal Planning:
- 14. B. Shopping for Healthy Foods:
- 15. C. Eating Out:
- 16. VI. Conclusion – A Guide to a Balanced and Healthy Diet
- 17. Frequently Asked Questions
- 18. References
Summary – A Guide to a Balance and Healthy Diet
- A balanced and healthy diet is essential for maintaining good health and preventing chronic diseases.
- It should include a variety of nutrient-rich foods from all food groups, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Portion control is important to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
- Drinking plenty of water and limiting sugary drinks is crucial for hydration and avoiding empty calories.
- Limiting processed and high-sugar foods is important for overall health.
- Regular physical activity should be combined with a healthy diet for optimal health benefits.
I. Introduction – A Guide to a Balanced and Healthy Diet
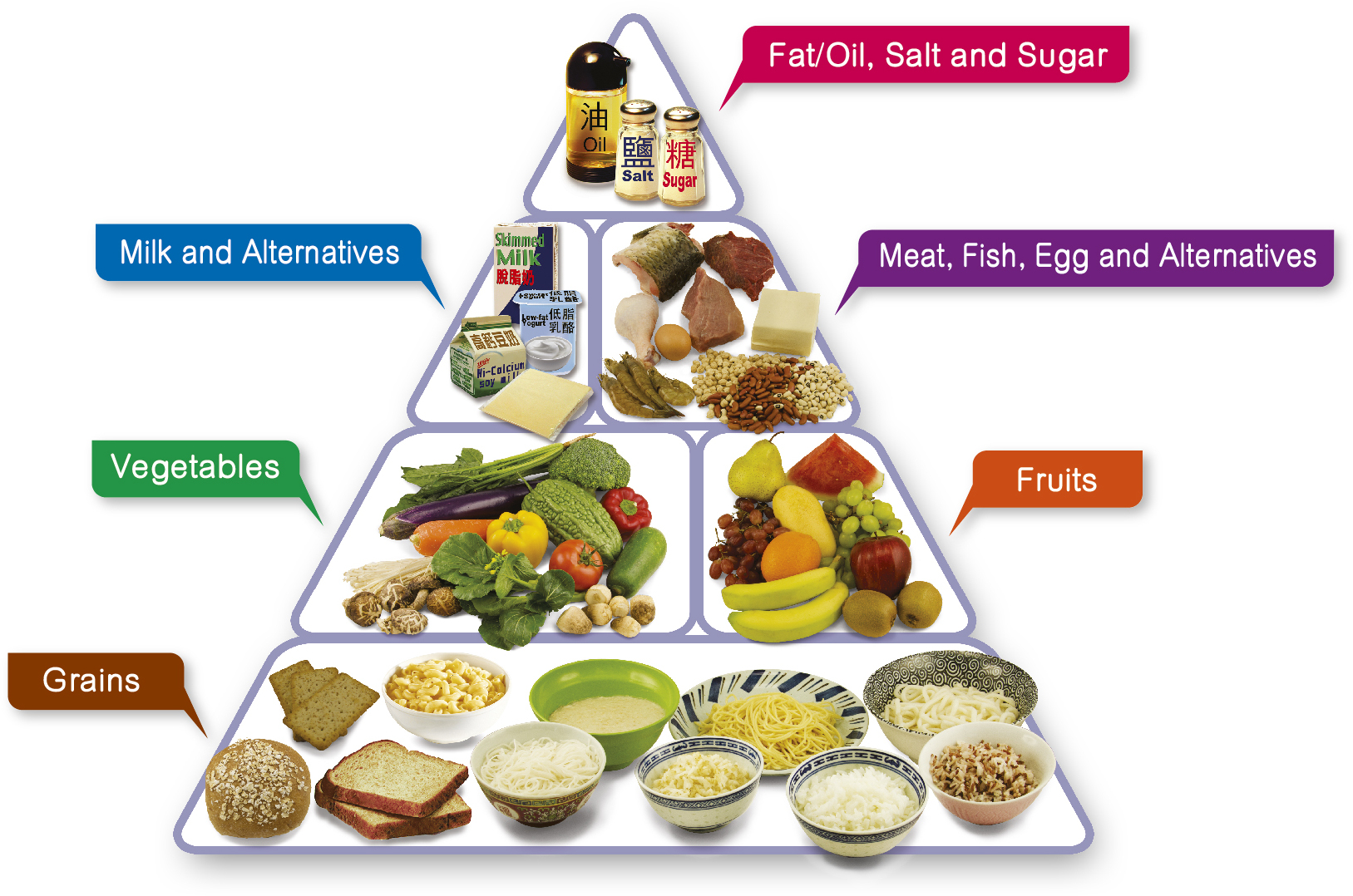

Maintaining a balanced and healthy diet is crucial for overall well-being and optimal physical and mental performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will provide detailed information and evidence-based recommendations to help you make informed choices about your nutrition. By following these guidelines, you can enhance your health, prevent chronic diseases, and improve your quality of life.
A. Understanding the Importance of a Balanced Diet
- Our bodies require a wide range of nutrients to function optimally.
- A balanced diet ensures that we obtain all these essential nutrients in the right proportions.
- It includes macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) and micronutrients (vitamins and minerals).
- A balanced diet provides an appropriate amount of energy to meet our individual requirements, preventing both undernutrition and overconsumption.
B. Key Components of a Balanced Diet
- Carbohydrates:
- Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for our bodies.
- Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates.
- They provide sustained energy and essential fiber.
- Proteins:
- Proteins are the building blocks of our body tissues.
- Lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts are rich sources of high-quality proteins.
- They support growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
- Fats:
- Healthy fats play a vital role in hormone production, absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and providing a concentrated source of energy.
- Incorporate sources of unsaturated fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil into your diet.
- Limit saturated and trans fats found in processed foods.
- Vitamins and Minerals:
- Essential vitamins and minerals are required in small amounts but have significant roles in various bodily functions.
- Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to ensure an adequate intake of these micronutrients.
C. Achieving Balance and Variety
- Balancing the quantity of food consumed is as important as the quality.
- Be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating and maintain a healthy weight.
- Aim to include foods from all major food groups in your diet.
- This ensures a diverse range of nutrients and reduces the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
- Opt for a colorful plate by incorporating different fruits and vegetables of various hues.
- Different colors signify different phytochemicals and antioxidants, which offer unique health benefits.
D. Evidence-Based Benefits of a Balanced Diet
- A balanced diet, coupled with regular physical activity, can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- It promotes the development of lean muscle mass while reducing the risk of obesity and related conditions.
- Numerous studies have shown that a balanced diet can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and hypertension.
- Emerging evidence suggests that a balanced diet may positively impact mental health.
- Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and antioxidants have been linked to improved mood, cognitive function, and reduced risk of depression and anxiety.
Stay tuned for the upcoming sections of this guide, where we will delve deeper into specific dietary recommendations for different age groups and address common dietary misconceptions.
II. Benefits of a Balanced and Healthy Diet
A. Improved Physical Health
A balanced and healthy diet is crucial for promoting and maintaining optimal physical health. It provides essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that support the overall functioning of the body and help prevent chronic diseases.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases:
A balanced and healthy diet lowers the risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancer. Including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet provides necessary nutrients and antioxidants that protect against these conditions. - Enhanced Heart Health:
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins significantly improves heart health. These foods are low in unhealthy fats, cholesterol, and sodium, which contribute to heart disease. They also contain heart-healthy nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants. - Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for physical health. A balanced diet, combined with regular physical activity, helps achieve and sustain a healthy weight. Nutrient-dense but low-calorie foods like fruits and vegetables can be incorporated into a balanced diet to promote satiety and prevent overeating.
B. Improved Mental Health
A balanced and healthy diet also plays a significant role in supporting mental well-being. The nutrients obtained from a varied diet positively affect brain function and contribute to improved mental health outcomes.
- Enhanced Cognitive Function:
Consuming a diet rich in nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals supports optimal brain function. These nutrients are found in foods such as fatty fish, nuts, seeds, whole grains, leafy greens, and legumes. Adequate intake of these nutrients improves memory, focus, and overall cognitive performance. - Reduced Risk of Mental Disorders:
A healthy diet may help reduce the risk of mental disorders like depression, anxiety, and age-related cognitive decline. Certain nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, have neuroprotective effects and may help prevent or delay the onset of these conditions.
C. Increased Energy Levels
A balanced and healthy diet significantly impacts energy levels throughout the day by providing the body with necessary nutrients.
- Balanced Macronutrient Intake:
A diet that includes a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats fuels the body and sustains energy levels. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy, while proteins and fats contribute to satiety and provide sustained energy. Including complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats in meals and snacks helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent energy crashes. - Adequate Hydration:
Proper hydration is essential for optimal energy levels. Dehydration can lead to fatigue and decreased cognitive function. Consuming an adequate amount of water and hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables prevents dehydration and supports energy levels.
By adopting a balanced and healthy diet, you can experience numerous benefits for physical and mental health. It reduces the risk of chronic diseases, promotes heart health, enhances cognitive function, reduces the risk of mental disorders, and increases energy levels. Prioritize a varied and nutrient-rich diet to optimize your overall well-being and lead a healthier lifestyle.
III. Essential Nutrients for a Balanced and Healthy Diet
A. Protein:
- Protein is essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
- Include a variety of protein-rich foods in your diet, such as lean meats, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based sources like tofu and tempeh.
- Adequate protein intake is vital for muscle growth and repair, as well as supporting the immune system.
B. Carbohydrates:
- Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy and essential for optimal brain function and physical performance.
- Choose complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, as they provide sustained energy and promote digestive health.
- Carbohydrates should typically make up around 45-65% of total daily calorie intake.
C. Healthy Fats:
- Choose healthy fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
- Limit saturated and trans fats found in animal products and processed foods, as they can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Healthy fats provide essential fatty acids, support brain health, and help maintain healthy skin and hair.
D. Vitamins and Minerals:
- Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet to ensure an adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals.
- Vitamins and minerals are involved in numerous bodily functions, including immune function, energy production, and bone health.
- They also play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin, eyes, and hair, as well as supporting cognitive function and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
E. Water:
- Water is essential for overall health and well-being.
- Aim for at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day (about 2 liters) to stay adequately hydrated.
- Proper hydration promotes optimal digestion, nutrient absorption, healthy skin, kidney function, and weight management. It is crucial for physical and cognitive performance.
Remember to consult with your healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific needs and goals.
IV. Eating Habits for a Balanced and Healthy Diet
A. Eating Regularly:
Eating regularly is important for a balanced and healthy diet. It helps regulate blood sugar levels, provides sustained energy, and prevents overeating. Aim for three main meals and two to three small snacks per day.
Benefits of Regular Eating:
– Stable Blood Sugar Levels: Regular meals prevent energy crashes and mood swings.
– Improved Digestion: Consistently eating promotes better digestion and nutrient absorption.
– Enhanced Metabolism: Regular meals keep the metabolism active, aiding in weight management.
Strategies for Regular Eating:
– Meal Planning: Plan your meals in advance to have balanced options available throughout the day.
– Set Reminders: Use alarms or smartphone apps to remind yourself to eat at regular intervals.
– Avoid Skipping Meals: Skipping meals can lead to overeating later and disrupt your body’s hunger cues.
B. Eating in Moderation:
Eating in moderation is crucial for a balanced and healthy diet. It involves portion control and being mindful of the quality and quantity of food.
Portion Control:
– Use Measuring Tools: Utilize measuring cups, spoons, or a food scale to accurately portion your meals and snacks.
– Mindful Eating: Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues, stopping eating when you feel satisfied but not overly full.
– Balance Macronutrients: Include a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats in each meal for satiety and prevention of overeating.
Quality over Quantity:
– Nutrient-Dense Foods: Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
– Limit Processed Foods: Minimize intake of processed and refined foods high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
– Enjoy Treats in Moderation: Indulge in favorite treats occasionally, but be mindful of portion sizes and frequency.
C. Eating a Variety of Foods:
Eating a variety of foods ensures your body receives essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals.
Nutritional Benefits:
– Balanced Nutrient Intake: Different foods offer different nutrients, so consuming a variety meets your body’s nutritional needs.
– Disease Prevention: A diverse diet is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
– Gut Health: A diverse range of foods supports a healthy gut microbiome, important for digestion and overall well-being.
Tips for Dietary Diversity:
– Include Colorful Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to consume a rainbow of fruits and vegetables for maximum nutrient intake.
– Try New Recipes and Ingredients: Experiment with different cuisines, recipes, and ingredients to expand your palate and food choices.
– Seasonal and Local Produce: Incorporate seasonal and locally sourced foods for fresh and diverse options.
By adopting these eating habits, you can promote a balanced and healthy diet that optimizes your overall well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice based on your specific dietary needs and health goals.
V. Strategies for Eating a Balanced and Healthy Diet
A. Meal Planning:
Meal planning is essential for a balanced and healthy diet. Here’s how you can effectively plan your meals:
- Understand your nutritional needs based on factors like age, gender, activity level, and any dietary restrictions or health conditions you may have.
- Consult with a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Create a weekly meal schedule for breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks to save time and make healthier choices.
- Include a variety of food groups like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats for essential nutrients.
- Opt for homemade meals using fresh, whole ingredients to control ingredients and portion sizes.
- Plan for leftovers to save time and effort on busy days.
B. Shopping for Healthy Foods:
Wise grocery shopping is crucial for a balanced and healthy diet. Follow these strategies:
- Prepare a detailed shopping list based on your meal plan to avoid unhealthy impulse purchases.
- Spend more time in the fresh produce, meat, dairy, and bakery sections located in the perimeter of the grocery store.
- Read and understand food labels, paying attention to serving size, nutrient content, and ingredients.
- Choose whole foods over processed options to retain natural nutrients.
- Be mindful of portion sizes and consider using measuring cups or a food scale.
C. Eating Out:
Maintaining a balanced and healthy diet while dining out is possible with these tips:
- Research the menu in advance and look for healthier options like grilled or baked proteins, salads, and vegetable-based dishes.
- Practice portion control by sharing an entree or packing half of your meal to go.
- Make special requests for dressings or sauces on the side, substituting fries for a side salad or steamed vegetables, or opting for grilled options.
- Be aware of hidden ingredients like added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excessive sodium.
- Stay hydrated with water and limit sugary beverages and alcohol.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can develop a habit of eating a balanced and healthy diet. Consistency and small, sustainable changes can lead to significant long-term benefits for your overall health and well-being.
VI. Conclusion – A Guide to a Balanced and Healthy Diet
Maintaining a balanced and healthy diet is essential for overall well-being and optimal functioning of the body. By following the guidelines outlined in this section, individuals can make informed choices about their food intake and ensure they are providing their bodies with the necessary nutrients for optimal health.
1. Understanding Macronutrients
- A balanced diet should consist of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
- Carbohydrates are the body’s primary source of energy and should mainly come from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins play a crucial role in building and repairing tissues and can be obtained from lean meats, poultry, fish, legumes, and dairy products.
- Healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, are essential for brain function and hormone production.
2. Importance of Micronutrients
- Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are vital for various bodily functions.
- Consuming a wide variety of fruits and vegetables ensures an adequate intake of these micronutrients.
- For example, vitamin C boosts the immune system and can be found in citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers.
- Calcium is essential for strong bones and can be obtained from dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified plant-based milk.
3. Hydration and Fluid Intake
- Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining overall health.
- Water is the best choice for hydration, and individuals should aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Other hydrating options include herbal teas and natural fruit juices, but it is important to limit the consumption of sugary beverages.
4. Portion Control and Mindful Eating
- Maintaining a healthy weight is closely tied to portion control and mindful eating.
- It is essential to listen to the body’s hunger and fullness cues and avoid overeating.
- Eating slowly, savoring each bite, and being mindful of the flavors and textures of food can help prevent overconsumption.
5. The Role of Fiber
- Including an adequate amount of dietary fiber in the diet is crucial for digestive health and preventing chronic diseases.
- Whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables are excellent sources of fiber.
- It is recommended to consume at least 25-30 grams of fiber per day.
6. Limiting Processed Foods and Added Sugars
- Processed foods often contain high amounts of unhealthy fats, added sugars, and sodium, which can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
- Opting for whole, unprocessed foods and limiting the intake of sugary snacks, sodas, and processed meats is essential for a balanced diet.
7. Individualized Approach
- Everyone’s nutritional needs may vary based on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and underlying health conditions.
- Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance to ensure dietary requirements are met.
Adopting a balanced and healthy diet is a lifelong commitment to nourishing the body with the right nutrients. By incorporating a variety of whole foods, practicing portion control, and being mindful of food choices, individuals can optimize their health and well-being. Remember, small changes can lead to significant improvements in overall health, so start making positive choices today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the guide to a balanced diet?
A balanced diet includes a variety of foods from different food groups. It should consist of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. It is important to limit the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats. Portion control is also crucial to maintain a balanced diet. It is recommended to drink plenty of water and limit the consumption of sugary beverages. Regular physical activity is also important to complement a balanced diet.
What are the 7 things needed for a balanced diet?
A balanced diet should include the following 7 things:
1. Fruits and vegetables: These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
2. Protein: Sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes are important for muscle repair and growth.
3. Whole grains: Foods like whole wheat bread, brown rice, and oats provide energy and fiber.
4. Dairy or dairy alternatives: Milk, cheese, and yogurt are good sources of calcium and vitamin D.
5. Healthy fats: Foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil provide essential fatty acids.
6. Water: Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health and bodily functions.
7. Limit added sugars and salt: Consuming too much can lead to health problems, so it’s important to moderate their intake.
What are 5 balanced diets?
A balanced diet includes a variety of foods from different food groups to provide all the necessary nutrients for good health. Here are five examples of balanced diets:
1. Mediterranean diet: This diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins (such as fish and poultry), and healthy fats (such as olive oil). It limits processed foods, red meat, and sugary beverages.
2. DASH diet: The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet focuses on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. It also limits sodium (salt) intake to help lower blood pressure.
3. Vegetarian diet: A vegetarian diet includes plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It excludes meat, poultry, and fish. It’s important to ensure adequate protein intake from plant sources.
4. Mediterranean-style vegetarian diet: This diet combines the principles of the Mediterranean diet with a vegetarian approach. It emphasizes plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate consumption of dairy products and eggs.
5. Flexitarian diet: This is a flexible approach that encourages mostly plant-based foods but allows for occasional consumption of meat and animal products. It focuses on whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes,
References
- 2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans. 8th edition. (2015, December)
https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/resources/2015-2020_Dietary_Guidelines.pdf - All about the vegetable group. (2018, January 3)
https://www.choosemyplate.gov/vegetables - Dietary guidelines and MyPlate. (2018, September 5)
https://www.choosemyplate.gov/dietary-guidelines - The American Heart Association’s diet and lifestyle recommendations. (2015, August 15)
https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/aha-diet-and-lifestyle-recommendations - What is MyPlate? (2018, December 14)
https://www.choosemyplate.gov/MyPlate - What’s a whole grain? A refined grain? (n.d.)
https://wholegrainscouncil.org/whole-grains-101/whats-whole-grain-refined-grain
This is a crucial subject—keep producing such remarkable content! Someone shared their personal weight loss story, highlighting the difficulties they encountered before discovering the Diet-To-Go Meal Service. They noted that the pre-portioned meals saved them time and supported their commitment to their goals. The conversation is a reminder of how essential balance is to the weight loss journey. For those who may find it useful, here’s the link they provided.
Did You Know? Cloudways makes cloud hosting a breeze, giving you a fast, friendly platform to build and grow your online presence.
Great insight! Managing cloud servers often seems complex, but Cloudways takes the stress out of the equation. Their platform delivers powerful performance without the usual technical headaches. It’s an ideal solution for those who want scalable hosting without getting lost in server configurations. Definitely worth checking out for a smoother hosting journey. Keep up the excellent work! Explore more through the link.
Speed is everything in eCommerce – this article breaks down the best hosting for WooCommerce.
Supercharge your online business with the ultimate managed hosting solution — experience speed, security, and simplicity with Cloudways!